• unique_ptr
특정 객체를 가리키는 하나의 스마트 포인터
복사 새성자와 복사 대입 연산자 불가능
- 사용법
unique_ptr<클래스> 스마트 포인터명(new 클래스)
unique_ptr<클래스> 스마트 포인터명 = make_unique<클래스>(인수);
가능하면 new로 하지 말고 make~로 할것
클래스를 스마트 포인터로 호출해보면 따로 delete 하지 않아도 소멸자가 자동으로 호출된다
class T {
public:
T() { cout << "create t" << endl; }
~T() { cout << "remove t" << endl; }
};
int main() {
unique_ptr<T> ptr = make_unique<T>();
cout << ptr.get() << endl;
}

- 상속관계
class T {
public:
T() { cout << "create t" << endl; }
~T() { cout << "remove t" << endl; }
};
class C : public T {
public:
C() { cout << "create c" << endl; }
~C() { cout << "remove c" << endl; }
};
int main() {
unique_ptr<C> ptr2 = make_unique<C>();
cout << ptr2.get() << endl;
}
위와 같은 상속 관계에서 잘 동작한다
-재귀 호출
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
void f1(); void f2(); void f3();
class Test {
int id;
public:
Test(int n) {
id = n;
cout << "생성자 " << id << endl;
}
~Test() {
cout << "소멸자 " << id << endl;
}
};
void f1() {
unique_ptr<Test> ptr = make_unique<Test>(1);
f2();
}
void f2() {
unique_ptr<Test> ptr = make_unique<Test>(2);
f3();
}
void f3() {
unique_ptr<Test> ptr = make_unique<Test>(3);
throw 10;
}
int main() {
try
{
f1();
}
catch (int x)
{
cout << "catch block" << endl;
}
cout << "main end";
}
재귀 호출에서도 생성자 1 2 3 소멸자 3 2 1 순으로 잘 호출된다
-move로 메모리 이동
unique_ptr<T> ptr1 = make_unique<T>();
cout << ptr1.get() << endl;
unique_ptr<T> ptr2 = make_unique<T>();
ptr1 = move(ptr2); // move 연산으로 메모리를 옮기는 것은 가능
• shared_ptr
특정 개체를 여러개의 스마트 포인터가 가리키고
공유시 +, 해제시 - 되는 reference count 라는 변수를 두어서 0이되 면 메모리 해제
shared_ptr<클래스> 스마트 포인터명 = make_shared<클래스>(인수);
- use_count 확인
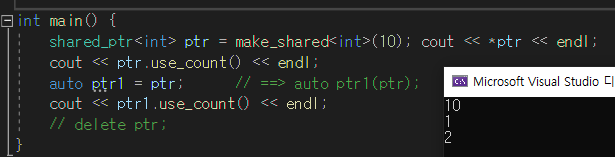
처음 생성하고 해제 안하면 1, 다른 데서 참조하면 2로 카운트가 증가했다
int main() {
shared_ptr<int> ptr = make_shared<int>(10); cout << *ptr << endl;
cout << ptr.use_count() << endl;
auto ptr1 = ptr; // ==> auto ptr1(ptr);
cout << ptr1.use_count() << endl;
}
- shared_pointer 순환 참조 문제
아래 코드는 서로 참조하는게 계속 유지되서 메모리 해제가 안된다
class Node {
public:
shared_ptr<Node> next;
Node() { cout << "Node Create\n"; }
~Node() { cout << "Node Deleted\n"; }
};
int main() {
shared_ptr<Node> p1 = make_shared<Node>();
shared_ptr<Node> p2 = make_shared<Node>();
p1->next = p2;
p2->next = p1;
}
• weak_ptr
shared_ptr가 가리키는 객체를 참조하면서 reference count는 증가시키지 않는다
shared_ptr의 참조 순환 문제를 해결하기 위해서 사용한다
메모리 접근시 멤버 함수 lock() 이용하여 접근한다
위 코드의 다음 노드를 가리키는 next를 weak_ptr로 바꾸면 참조 순환 문제가 해결되어 소멸자가 호출된다
class Node {
public:
weak_ptr<Node> next;
Node() { cout << "Node Create\n"; }
~Node() { cout << "Node Deleted\n"; }
};
int main() {
shared_ptr<Node> p1 = make_shared<Node>();
shared_ptr<Node> p2 = make_shared<Node>();
p1->next = p2;
p2->next = p1;
}
-lock을 이용한 weak_ptr 메모리 접근
int main() {
shared_ptr<int> ptr1 = make_shared<int>(1);
weak_ptr<int> ptr2 = ptr1;
cout << "ptr1/ptr2 use_count" << endl;
cout << ptr1.use_count() << endl;
cout << ptr2.use_count() << endl;
*ptr1 = 100;
cout << "*ptr1 = " << *ptr1 << endl;
cout << "*ptr2 = " << *(ptr2.lock()) << endl;
}'대외활동 > 시스템프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 0805 QT C++ 다양한 ui, 시그널 (0) | 2024.08.05 |
|---|---|
| modern c++ (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| 예외 처리 (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| c++ 입출력 시스템 (1) | 2024.07.30 |
| 람다식 (0) | 2024.07.30 |

