• constexpr
C++에서는 매크로보다 constexpr 상수로 사용하는 걸 권장한다
#define SIZE 10 // C-style
constexpr int size = 10; // modern C++
• 초기화
중괄호 안에 다 박을 수 있다
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct S {
string name; float num;
S(string s, float f) : name(s), num(f) {}
};
int main() {
S s1("Norah", 2.7);
S s2("Frank", 3.5);
S s3("Jeri", 85.9);
// Basic initialization
vector<S> v;
v.push_back(s1);
v.push_back(s2);
v.push_back(s3);
// 모던 c++
vector<S> v2{ s1, s2, s3 };
vector<S> v3{ {"Norah", 2.7}, {"Frank", 3.5}, {"Jeri", 85.9} };
}
• 타입 캐스팅
- const_cast
const 변수에서 const 속성을 제거하기 위한 형 변환
string s1("abc");
const string* pStr1 = &s1;
pStr1->Set("def"); // const가 있는 상수이므로 재정의가 불가능
string* pStr2 = const_cast<string*>(pStr1); // const 속성을 제거, 재정의가 가능해진다
pStr2->Set(“def”);
- static_cast
(int)나 (string)으로 형 변환하는 C 타입 캐스팅이 아닌 c++식 형 변환
컴파일 시점에 캐스팅
형 변환이 가능하면 형 변환을 수행하고, 형 변환이 불가능하면 컴파일 x
enum class COLOR{ red, green, blue};
int main() {
int color = static_cast<int> (COLOR::green);
cout << color;
}
- dynamic_cast
typeid 연산자를 통해 클래스 타입 정보를 알 수 있다
런타임에 캐스팅한다
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
class P {
public:
P() {}
virtual ~P(){}
virtual void show() { cout << "parent\n"; }
};
class C : public P {
public:
C(){}
~C(){}
void show() { cout << "child\n"; }
};
int main() {
P* ptr = new P();
cout << typeid(ptr).name() << endl;
}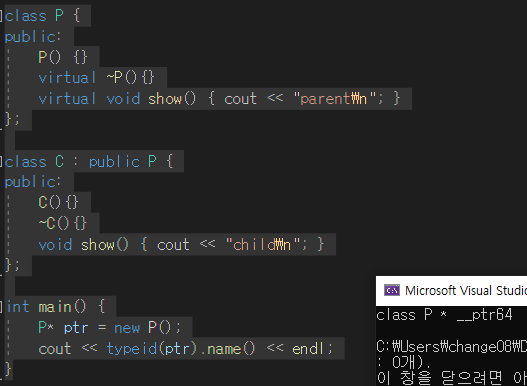
위의 P와 C 클래스를 런타임에 캐스팅, 자식 메서드의 show가 호출된다
P* ptr = new C();
C* cptr = dynamic_cast<C*>(ptr);
if (cptr == nullptr)
{
cout << "cast fail";
}
else cout << "cast success";
cptr->show();'대외활동 > 시스템프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 0807 QT 에디터 & 액션 (0) | 2024.08.07 |
|---|---|
| 0805 QT C++ 다양한 ui, 시그널 (0) | 2024.08.05 |
| 스마트 포인터 (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| 예외 처리 (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| c++ 입출력 시스템 (0) | 2024.07.30 |


